What are the three stages of Syphilis?
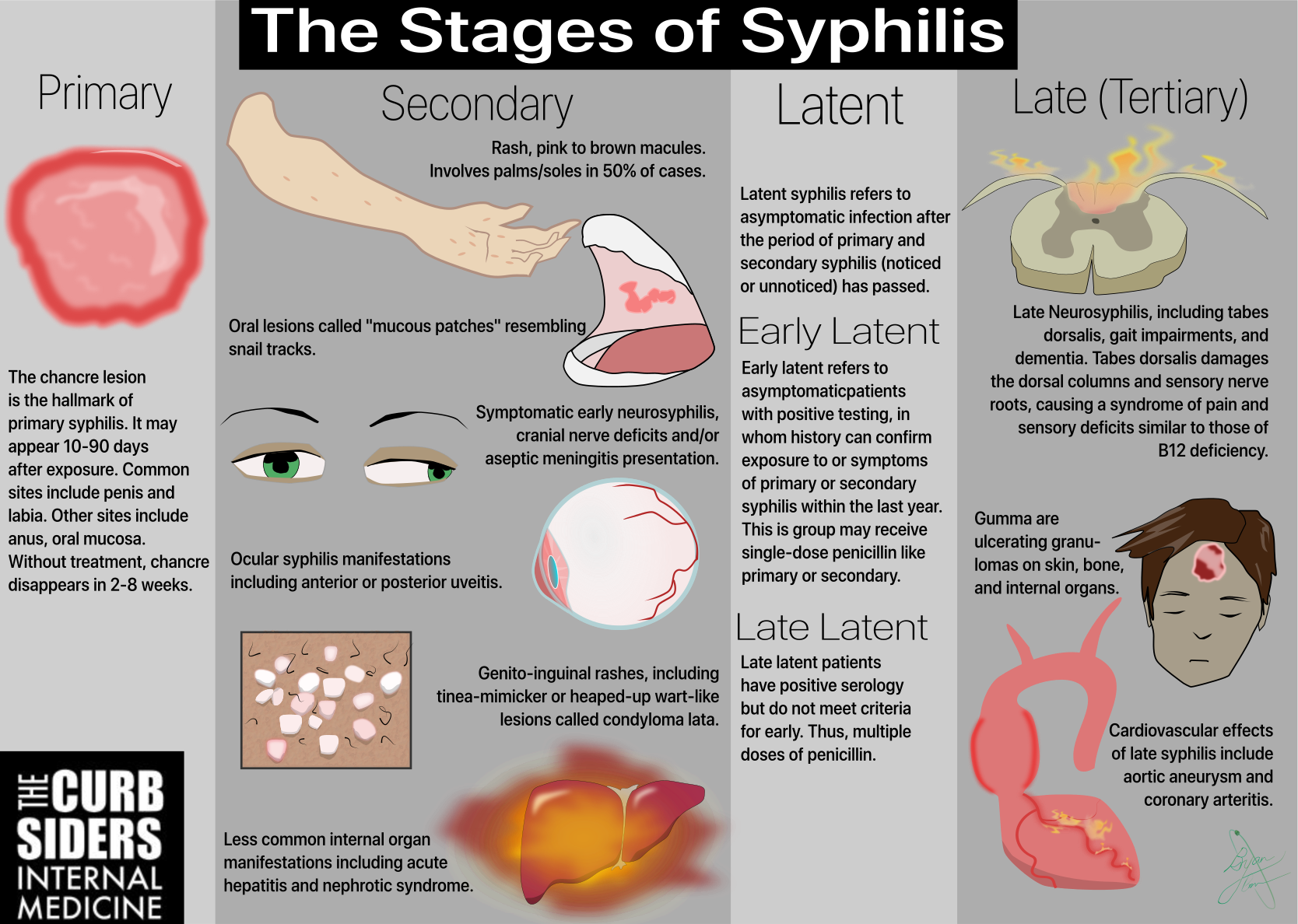
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) which can lead to life-threatening consequences if left untreated. Syphilis progresses in three prominent stages: primary, secondary and tertiary. A Syphilis infection can be easily cured and treated in the earlier stages, so it’s important to understand which symptoms to look out for before the infection is able to cause permanent damage.
1. The primary stage
The first common symptom of Syphilis is the appearance of a painless sore, usually solitary, also known as a ‘chancre’. This appears in the genital area or around the mouth between 10 and 90 days after infection. If you can’t see it, because it’s in the throat or anus, you will not know you have it because it doesn’t hurt. The sore will normally heal and disappear within two to six weeks. Glands located near the sore, such as in the neck or groin, may become larger during this time.
2. The secondary stage
If the infection is left untreated during the primary stage, a few weeks later you may begin to feel ill with a headache or fever. You may develop a rash all over your body, and sometimes noticeably on the hands or feet. Other possible symptoms include hair loss, fatigue, or weight loss. Both men and women may notice skin growths around the genital area, particularly the anus. Women should also look out for abnormal skin around the vulva and vagina.
Secondary Syphilis will also seem to go away on its own, but will return, with several outbreaks before proceeding to the next stage.
Between the second and third stage, known as the ‘latent’ stage, many people with a Syphilis infection will not experience any symptoms.
3. The third stage
Over the following years, Syphilis can cause serious damage to important organs, including the heart, brain, and nervous system. At this stage, a Syphilis infection can be fatal.
Don’t risk it; get tested for Syphilis
Many of these symptoms can be mistaken for other STIs or health problems, so if you may have been at risk, it is vital that you get tested. A Syphilis infection needs to be treated and will not disappear on its own. In the Middle East, we can test for you for Syphilis just nine days after potential exposure, so don’t wait. Book your confidential appointment online or contact our Sexual Health Advisors today.

Don’t leave your sexual health to chance.
This article has been medically reviewed Dr. Steve Chapman, 29/08/2025.
Categories
- Abu Dhabi
- Bacterial Vaginosis
- Bahrain
- Blood Tests
- Cancer
- Cervical Cancer
- Chlamydia
- Dubai
- Fertility
- Gardnerella
- Genital Warts
- Gonorrhoea
- Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
- Herpes
- HIV (AIDS)
- HIV Testing
- HPV
- Instant Testing
- Kuwait
- Locations
- Middle East
- Mycoplasma
- Oman
- PAP Smear
- Positive STI Results
- Qatar
- Saudi Arabia
- Sex Education
- Sexual Health
- Sexual Health News
- Sexually Transmitted Infections
- STD Symptoms
- STD Tests and Screens
- STI Results
- STI Treatment
- STIs
- Sustainability
- Swab Tests
- Syphilis
- Trichomoniasis
- Uncategorized
- United Arab Emirates
- Ureaplasma
- Urine Tests




