Are HIV symptoms in women different than in men?
Symptoms can be a tricky issue when talking about STIs.
While most STIs are asymptomatic, certain symptoms can indicate the presence of an infection. And when these symptoms appear, it’s important to get tested and treated as soon as possible.
However, not all STIs have the same symptoms, and even the same STI can present differently in different people.
In this blog, we’ll look at how STIs present differently in both men and women, review what HIV is, and how it may present differently in women.
Keep reading to find out more.

Are you worried about HIV? Book a test at a local sexual health clinic today.
Do STI symptoms differ between the sexes?
In a word, yes. Sometimes.
Every infection presents differently depending on the person in question. The symptoms that one person experiences will not necessarily be what another person experiences.
Let’s take Gonorrhoea as an example.
Gonorrhoea, one of the most common bacterial STIs in the world, can present differently in men and women. When symptoms do occur, they can vary slightly based on sex organs.
For women, Gonorrhoea may cause an unusual discharge from the vagina. This discharge is composed of pus and plasma and may sometimes also contain normal vaginal discharge. It often has a yellowish or greenish colour and may also be tinged with blood. Women may also experience lower abdominal pain (which may be more noticeable during sex) and irregularities in their menstrual cycle.
Men may also experience discharge from the tip of their penis during a Gonorrhoea infection. However, this discharge may be a different colour and consistency than the discharge women experience. Male discharge during a Gonorrhoea infection can appear yellowish or green, but occasionally may even be watery or simply more abdundant.
The symptoms of Gonorrhoea can also differ in other ways. When Gonorrhoea goes untreated in a woman, she may develop Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, which could result in ectopic pregnancies and difficulty conceiving.
In men, Gonorrhoea may cause epididymitis, a swelling of the epididymis (the tube the semen travels through), which over time can also cause fertility problems, especially if the infection reaches the testicles.
What about other STIs?
The differences don’t end with Gonorrhoea. Many STI symptoms can manifest differently in women and men.
- HPV: Certain high-risk strains of HPV can cause changes in the cells of the cervix, leading to precancerous growths. HPV is the leading cause of cervical cancer in women.
- Chlamydia: Like Gonorrhoea, a Chlamydia infection can cause a different kind of discharge in men and women. In men, the discharge tends to be white, cloudy or watery. It can also cause the abdominal pain mentioned above, and unexpected menstrual bleeding. However, Chlamydia tends to be a much more asymptomatic infection than Gonorrhoea.
- Trichomonas: A Trichomonas infection can also cause differing forms of discharge in men and women, with women typically noticing a change in smell.
But that’s other STIs. What about HIV?
What is HIV?
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a blood-borne sexually transmitted infection that tends to transmit through unprotected sexual intercourse, like oral, vaginal, or anal sex. The virus can also be transmitted through other means, like shared needles for intravenous drug use, unsterilised tattooing equipment, and blood transfusions.
A chronic HIV infection, if left untreated, can lead to acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). AIDS describes the reduced ability of the immune system to fight infections and illnesses, often leading to life-threatening complications.
HIV in the Middle East
In the Middle East, HIV is suspected to be on the rise, especially among three types of populations: people who inject drugs, men who have sex with men, and female sex workers.
However, this rise is also occurring in the general population. Treating HIV in the region remains difficult because of underfunding, poor monitoring, and social stigma.
There are around 240,000 people living with HIV in the Middle East and North Africa, with around 20,000 new cases reported each year.
However, because of the serious effects of an untreated HIV infection, the social stigma connected to the infection, and various legal reasons, Better2Know sees a large demand among its patients in the Middle East for HIV testing.
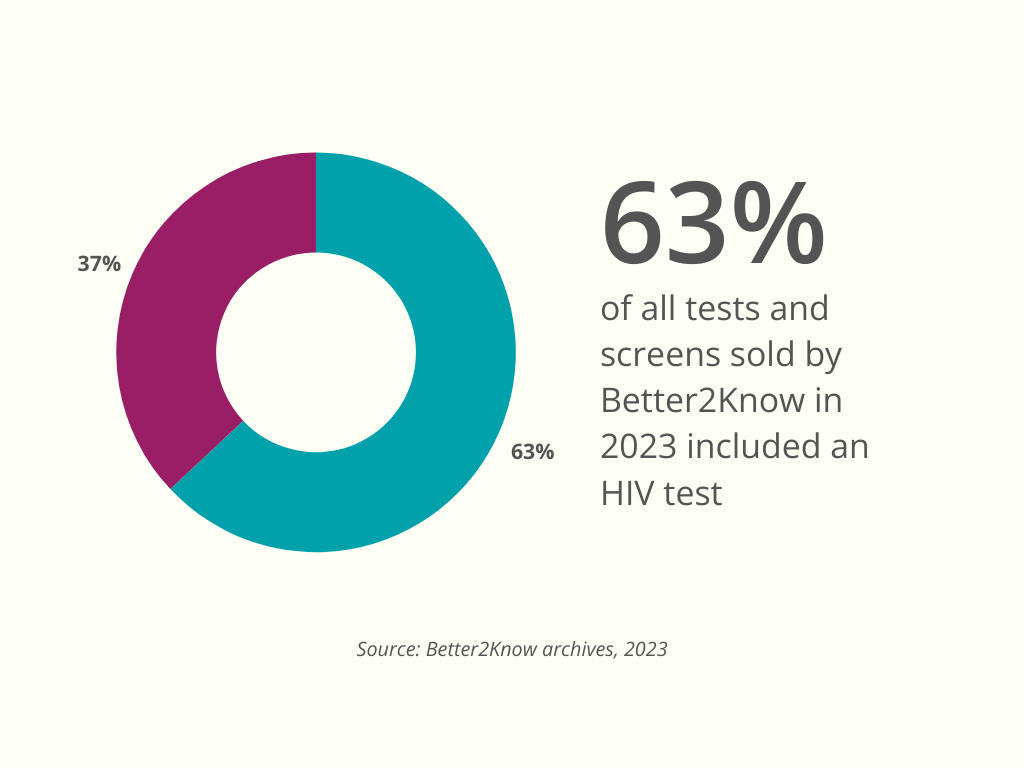
Around 63% of all tests and screens sold by Better2Know in the Middle East were either individual tests for HIV or screens that included a test for HIV.
The power of treating HIV
It’s important to stress that most people who have HIV, provided they get the support and treatment they need, can lead normal, healthy lives.
Antiretroviral therapy can reduce the likelihood of transmitting the infection by reducing the infected person’s viral load to undetectable levels, making it effectively impossible that they will pass on the virus to another person.
Don’t put off getting tested. Book your HIV screen today.
What are the symptoms of HIV?
Like other STIs, someone may have an HIV infection and not have any early symptoms. Many people can go months, years, or even decades without knowing they have HIV.
When HIV symptoms do appear, they tend to appear in the initial stages of the infection, usually within the first six weeks. The symptoms of an acute HIV infection can include:
- Unintentional weight loss
- Diarrhoea
- Skin rashes, especially on your face, genitals, or anus
- An increase in Herpes ulcers or thrush infections in your mouth and genitals
- Sweats, especially at night
- Exceptional and unusual tiredness
- Nausea or loss of appetite
- Swollen lymph glands in the neck, groin, or armpits
What makes diagnosing HIV so tricky is that many of the above symptoms are shared by other, less serious infections. Someone may get one or more of these symptoms and write them off as the flu. This person may dismiss these flu-like symptoms as an unserious infection and not seek testing or treatment. (Of course, patients can also catch the flu while in the throes of an acute HIV infection.)
What HIV symptoms do only women experience?
Unlike bacterial STIs that are site-specific and infect the genitals, the symptoms of HIV in men and women are largely the same.
However, several symptoms that are specific to women can occur during the early and later stages of the infection.
HIV symptoms in women can include:
- Frequent yeast infections
- Vaginal burning or soreness
- Irregular periods
- Bleeding or spotting between periods
- Pelvic pain
- Pain during sex
- Increased flow during periods
- Watery or bloody vaginal discharge
Women who have HIV are also more susceptible to certain other long-term conditions, including entering menopause at an earlier age, osteoporosis, more rapid transition of HPV into cervical cancer, and the risk of passing on HIV to their baby during pregnancy or childbirth.
There is also some evidence to suggest that women may experience a quicker disease progression than men.
Final thoughts
If you’re worried about HIV, you should get tested. It’s always better to know to secure your peace of mind.
Call the number at the top of this page to speak to one of our trained Sexual Health Advisors. They can discuss your situation with you and help you choose a test or screen that will meet your needs.
You can also click the “Book Now” button to secure your online booking at a sexual health clinic near you.

Book your HIV test today.
This blog has been medically reviewed by Dr. Steve Chapman, 02/01/2024.
Categories
- Abu Dhabi
- Bacterial Vaginosis
- Bahrain
- Blood Tests
- Cancer
- Cervical Cancer
- Chlamydia
- Dubai
- Fertility
- Gardnerella
- Genital Warts
- Gonorrhoea
- Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
- Herpes
- HIV (AIDS)
- HIV Testing
- HPV
- Instant Testing
- Kuwait
- Locations
- Middle East
- Mycoplasma
- Oman
- PAP Smear
- Positive STI Results
- Qatar
- Saudi Arabia
- Sex Education
- Sexual Health
- Sexual Health News
- Sexually Transmitted Infections
- STD Symptoms
- STD Tests and Screens
- STI Results
- STI Treatment
- STIs
- Sustainability
- Swab Tests
- Syphilis
- Trichomoniasis
- Uncategorized
- United Arab Emirates
- Ureaplasma
- Urine Tests




